Publications
Publications categorized by topic and ordered in reverse chronological order.
2026
- QML.6G
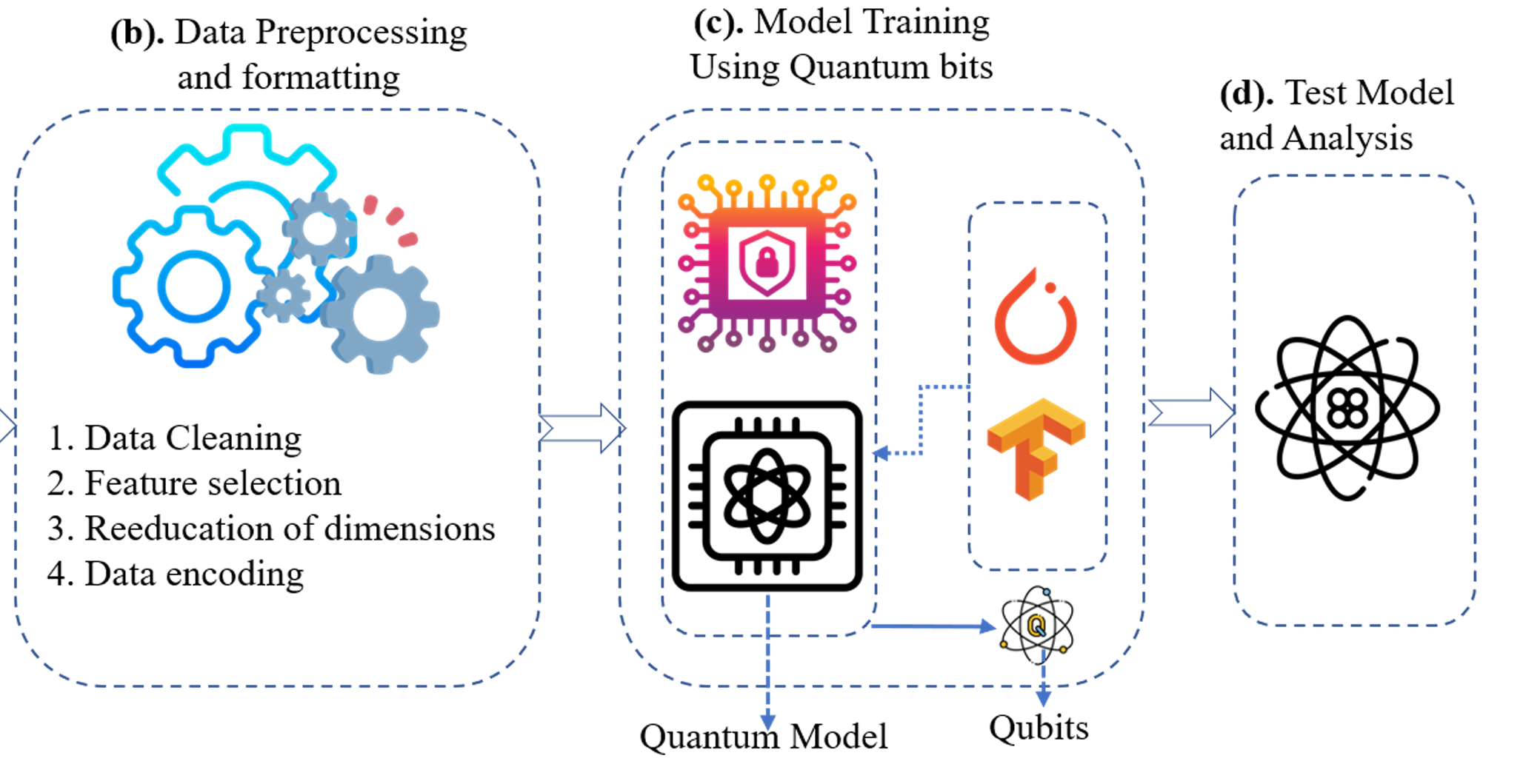 Integrating Quantum Computing and Machine Learning in 6G NetworksOgobuchi D Okey, Theodore T Chiagunye, Henrietta U Udeani, Nicholas Ikechukwu, and 2 more authorsQuantum Computing and Machine Learning for 6G, 2026
Integrating Quantum Computing and Machine Learning in 6G NetworksOgobuchi D Okey, Theodore T Chiagunye, Henrietta U Udeani, Nicholas Ikechukwu, and 2 more authorsQuantum Computing and Machine Learning for 6G, 2026The sixth-generation (6G) wireless networks are anticipated to have a transformative impact on communication methods, facilitating high-speed data transfer rates, extensive connectivity, and applications with minimal latency. The escalating intricacy and magnitude of 6G networks present noteworthy obstacles for conventional computing paradigms. In order to tackle these obstacles, the integration of quantum computing (QC) and machine learning (ML) methodologies within the framework of 6G networks is needed to improve its robustness and handle issues relating to resource allocation, bandwidth, and spectrum management. This chapter provides a thorough examination of the latest advancements in the field of fusing QC and ML to cater to the requirements of 6G technology. We highlight and discuss how quantum computing’s unique features, like superposition and entanglement, could improve the effectiveness of machine learning algorithms in the context of 6G networks. Additionally, this study explores the utilization of quantum machine learning (QML) techniques within the confines of 6G, aimed at improving the dynamics required to meet the sophisticated architecture of 6G. On top of the foregoing, we explore in detail the security implications and frameworks for implementing QML in 6G networks. Quantum cryptography methods, exemplified by quantum key distribution, offer heightened protection against unauthorized access and data breaches, thereby safeguarding the confidentiality and integrity of data conveyed through 6G networks. Ultimately, the benefits of QML and a roadmap outlining potential avenues for future research in this nascent field are presented. The study highlights the importance of the creation of quantum computing architectures that are both scalable and fault-tolerant, as well as the development of QML algorithms, which are optimized for 6G networks. The findings of this research are robust and enable students to gain in-depth knowledge of the concept of QML and assist in further research.
2025
- DORI
 Right side up? disentangling orientation understanding in mllms with fine-grained multi-axis perception tasksKeanu Nichols, Nazia Tasnim, Yuting Yan, Nicholas Ikechukwu, and 3 more authorsarXiv preprint arXiv:2505.21649, 2025
Right side up? disentangling orientation understanding in mllms with fine-grained multi-axis perception tasksKeanu Nichols, Nazia Tasnim, Yuting Yan, Nicholas Ikechukwu, and 3 more authorsarXiv preprint arXiv:2505.21649, 2025Object orientation understanding represents a fundamental challenge in visual perception critical for applications like robotic manipulation and augmented reality. Current vision-language benchmarks fail to isolate this capability, often conflating it with positional relationships and general scene understanding. We introduce DORI (Discriminative Orientation Reasoning Intelligence), a comprehensive benchmark establishing object orientation perception as a primary evaluation target. DORI assesses four dimensions of orientation comprehension: frontal alignment, rotational transformations, relative directional relationships, and canonical orientation understanding. Through carefully curated tasks from 11 datasets spanning 67 object categories across synthetic and real-world scenarios, DORI provides insights on how multi-modal systems understand object orientations. Our evaluation of 15 state-of-the-art vision-language models reveals critical limitations: even the best models achieve only 54.2% accuracy on coarse tasks and 33.0% on granular orientation judgments, with performance deteriorating for tasks requiring reference frame shifts or compound rotations. These findings demonstrate the need for dedicated orientation representation mechanisms, as models show systematic inability to perform precise angular estimations, track orientation changes across viewpoints, and understand compound rotations - suggesting limitations in their internal 3D spatial representations. As the first diagnostic framework specifically designed for orientation awareness in multimodal systems, DORI offers implications for improving robotic control, 3D scene reconstruction, and human-AI interaction in physical environments